Computing Limits from Graphs#
Example 1#
Evaluate limits based on the graph of a function
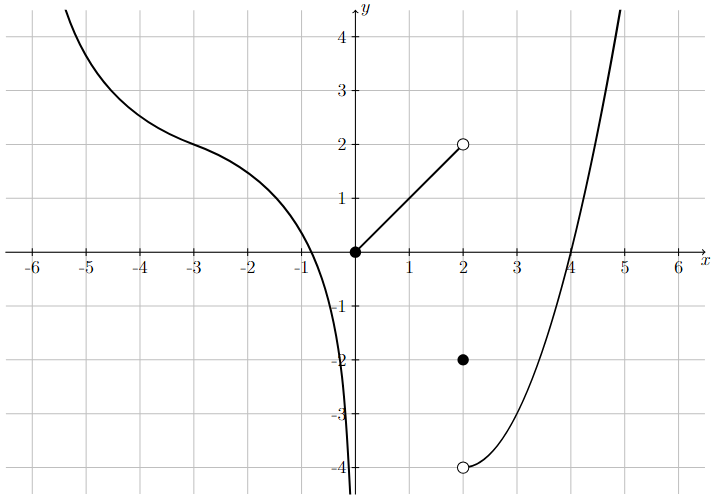
Let \(f(x)\) be defined by the following graph.
Evaluate \(\lim\limits_{x \to a^-} f(x)\), \(\lim\limits_{x \to a^+} f(x)\), and \(\lim\limits_{x \to a} f(x)\) for \(a = -3, 0, 2\).
Long Text Description
There is a horizontal x-axis with the points -6, -5, -4, -4, -2, -1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 marked. There is a vertical y-axis with the points -4, -3, -2, -1, 1, 2, 3, and 4. The graph of a discontinuous function is plotted on these axes. From left to right, the function decreases from positive infinity and goes down to negative infinity as x moves right towards 0, the function increases linearly from a filled in point at (0,0) to a hollow point at (2,2), jumps to a filled in point at (2,-2), continues from a hollow point at (2,-4) upward to positive infinity on the right.
Step 1: Evaluate the limit as \(x\) approaches \(-3\)
The two one-sided limits both exist and are both equal to 2.
Therefore, the limit exists and \(\lim\limits_{x\to -3} f(x) = 2.\)
Step 2: Evaluate the limit as \(x\) approaches \(0\)
The limit from the left does not exist and the limit from the right exists and is equal to 0.
Therefore, \(\lim\limits_{x\to 0} f(x)\) does not exist. Observation: If either of the one-sided limits does not exist (DNE) as \(x\) approaches \(a\), then the \(\lim\limits_{x\to a} f(x)\) does not exist.
Step 3: Evaluate the limit as \(x\) approaches \(2\)
The two one-sided limits both exist, but are not equal to each other.
Therefore, \(\lim\limits_{x\to 2} f(x)\) does not exist.
Example 2#
Evaluate limits based on the graph of a function
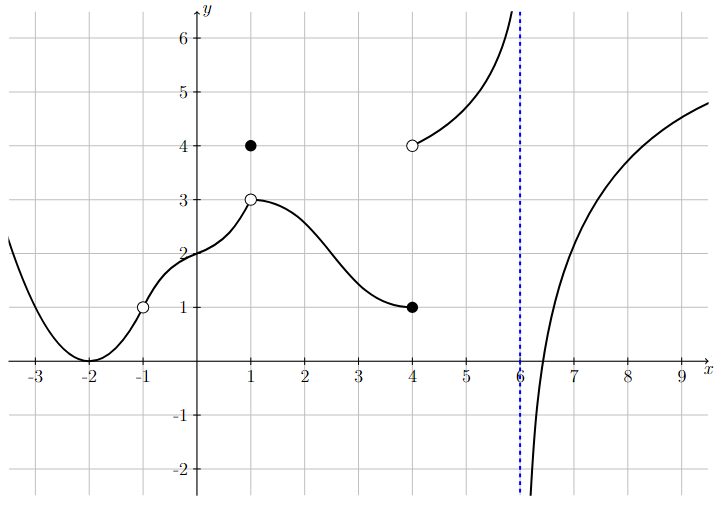
Let \(f(x)\) be defined by the following graph.
Evaluate \(\lim\limits_{x \to a^-} f(x)\), \(\lim\limits_{x \to a^+} f(x)\), and \(\lim\limits_{x \to a} f(x)\) for \(a = -1, 1, 4, 6\).
Long Text Description
There is a horizontal x-axis with the points -3, -2, -1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 marked. There is a vertical y-axis with the points -2, -2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 marked. There is a blue dotted vertical line at x = 6. The graph of a discontinuous function is plotted on these axes. From left to right, the function decreases as it comes in from the left, increases from rounded corner at (-2,0) to a hollow point at (-1,1), increases from that point to another hollow point at (1,3), jumps to a filled in point at (1,4), jumps back to the hollow point at (1,3) and decreases from there to a filled in point at (4,1), jumps to a hollow point at (4,4) and increases up to infinity as x approaches the blue dotted line at x = 6 from the left, and comes up from negative infinity to the right of the blue dotted line and increases as it goes off to the right.
Step 1: Evaluate the limit as \(x\) approaches \(-1\)
The two one-sided limits both exist and are both equal to 1.
Therefore, the limit exists and \(\lim\limits_{x\to -1} f(x) = 1\). Observation: Although \(f(-1)\) is not defined, the limit as \(x\) approaches \(-1\) still exists.
Step 2: Evaluate the limit as \(x\) approaches \(1\)
The two one-sided limits both exist and are both equal to 3.
Therefore, the limit exists and \(\lim\limits_{x\to 1} f(x) = 3\). Observation: Although \(f(1)\) is defined, it is not equal to the value of the limit as \(x\) approaches \(1\).
Step 3: Evaluate the limit as \(x\) approaches \(4\)
The two one-sided limits both exist, but are not equal to each other.
Therefore, \(\lim\limits_{x\to 4} f(x)\) does not exist.
Step 4: Evaluate the limit as \(x\) approaches \(6\)
Neither one-sided limit exists.
Therefore, \(\lim\limits_{x\to 6} f(x)\) does not exist.
